Patients and Care Givers | Types of Cancer | Prostate
About Prostate Cancer
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland that helps produce semen. It’s located under the bladder, in front of the rectum, and surrounds part of the urethra, which is the tube that carries urine and semen. Within the cells of the body lies DNA, which contains instructions for the cells. If the DNA tells cells to grow and divide faster than normal cells, an abnormal growth of accumulated cells, or a tumor, can develop into cancer.
My daughter said (prostate cancer) was an old black man’s disease. She said something else is going to kill you before that … but I wanted it treated and out of the body so that it did not spread to other areas of the body that are not as predictable for an old black man."
Amos Tingle

The cancer cells of malignant tumors can break away and travel to other parts of the body (metastasize). Benign tumors are non-cancerous tumors and do not metastasize. If a malignant growth is removed, the cancer cells can still grow back. If a benign growth is removed, it may not grow back or it may grow back slowly.
Prostate cancer occurs when there is abnormal cell growth in the prostate. The cause of prostate cancer is unknown; however, researchers do know that the growth of both normal and cancer cells is stimulated by male hormones such as testosterone.
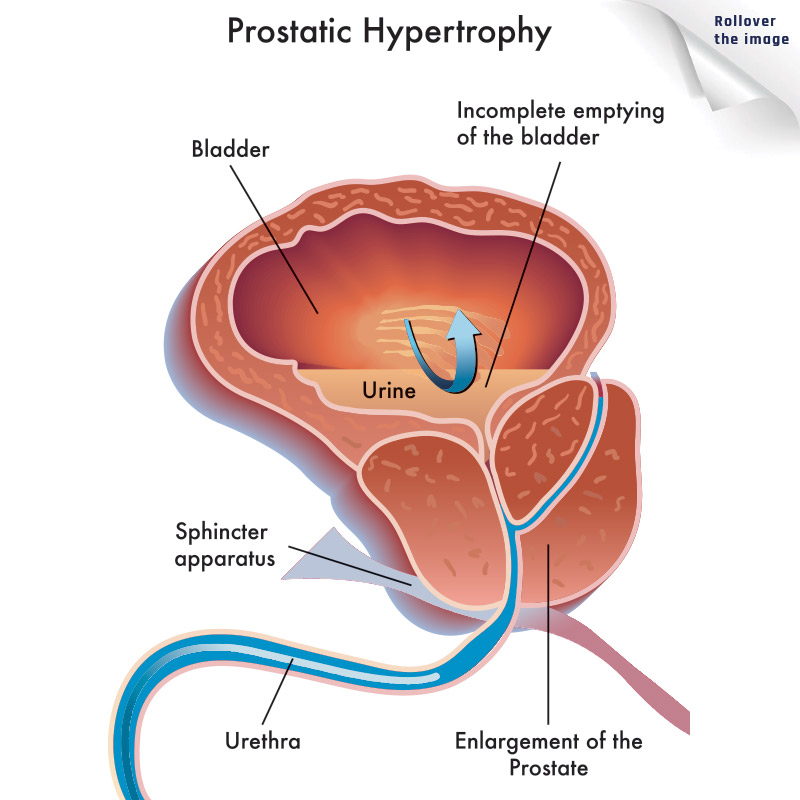
Localized prostate cancer is when cancer cells are confined to the prostate. If cancer cells grow large enough and become a tumor, it can put pressure on nearby organs and cause symptoms like difficulty urinating or frequent urination. Advanced prostate cancer is when cancer cells metastasize to other organs and/or bones.1
Watch Our Animation
To better understand how prostate seed brachytherapy works, watch our informative animation. It provides a simplified overview of the procedure, highlighting its benefits and effectiveness in treating prostate cancer.
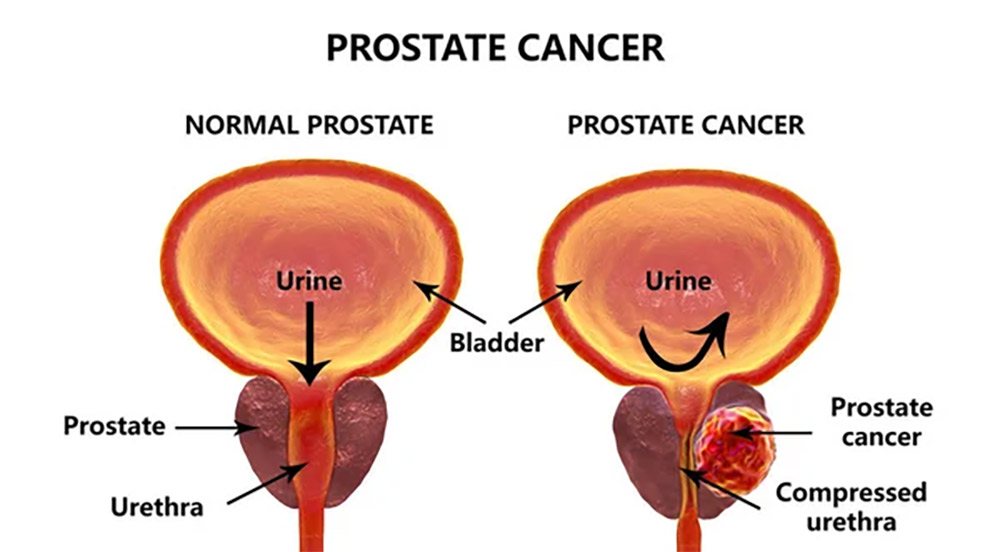
How Prostate Cancer Occurs
Prostate cancer occurs when there is abnormal cell growth in the prostate. The cause of prostate cancer is unknown; however, researchers do know that the growth of both normal and cancer cells is stimulated by male hormones such as testosterone.
Localized prostate cancer is when cancer cells are confined to the prostate. If cancer cells grow large enough and become a tumor, it can put pressure on nearby organs and cause symptoms like difficulty urinating or frequent urination. Advanced prostate cancer is when cancer cells metastasize to other organs and/or bones.1
Showing a normal prostate vs an enlarged prosate
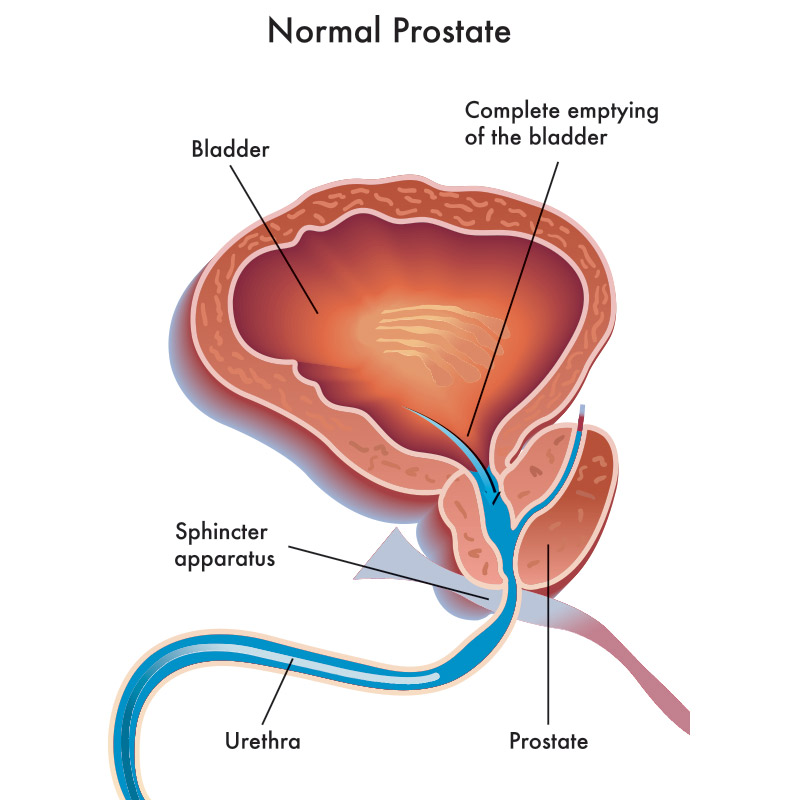
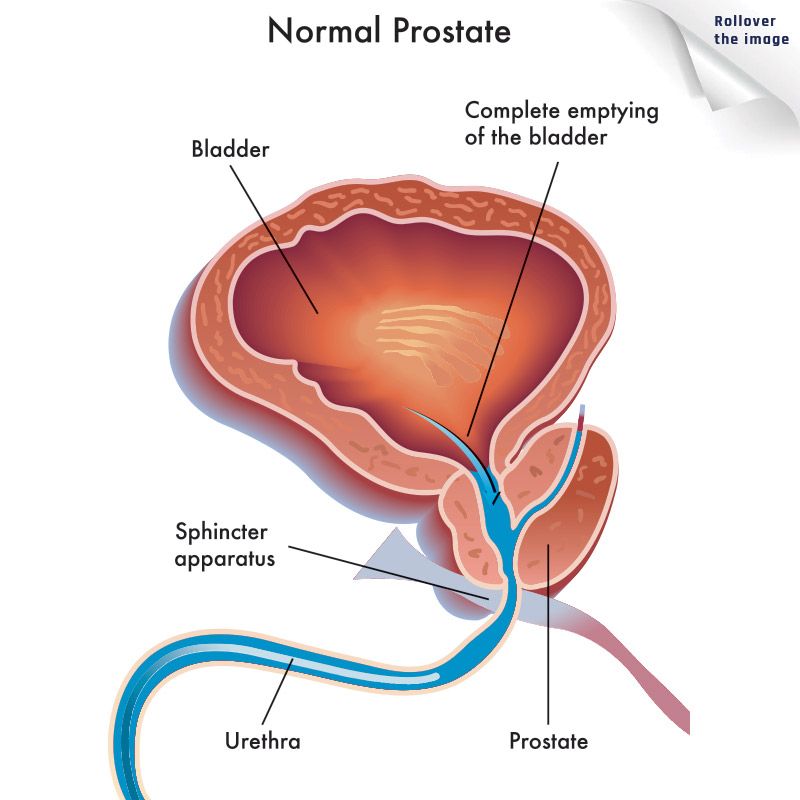
Rollover the image
Related pages
Proud Supporters of Men's Health Month:






June 2025
is Men’s Health Month.
This year, we’re focusing on closing the #EmpathyGap in men’s health, recognizing that men die 6 years earlier than women due to preventable health issues.
It’s time to bring empathy back and prioritize men’s well-being.
Connect with Us
Stay connected.
Join our Life after Seeds Facebook Group